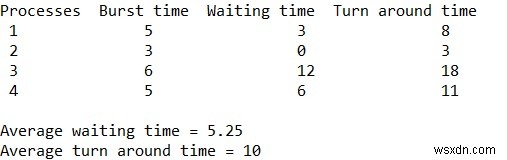กำหนดกระบวนการ เวลาระเบิดของกระบวนการตามลำดับและขีดจำกัดควอนตัม ภารกิจคือการค้นหาและพิมพ์เวลารอ เวลาตอบสนอง และเวลาเฉลี่ยตามลำดับโดยใช้วิธีการจองก่อนการจัดกำหนดการที่สั้นที่สุด
งานแรกที่สั้นที่สุดในการจัดตารางงานแรกคืออะไร
การจัดกำหนดการงานครั้งแรกที่สั้นที่สุดคืออัลกอริธึมการจัดกำหนดการงานหรือกระบวนการที่เป็นไปตามระเบียบวินัยการจัดกำหนดการที่ไม่ยึดเอาเสียก่อน ในสิ่งนี้ ตัวกำหนดตารางเวลาจะเลือกกระบวนการจากคิวรอโดยมีเวลาเสร็จสิ้นน้อยที่สุด และจัดสรร CPU ให้กับงานหรือกระบวนการนั้น Shortest Job First เป็นที่ต้องการมากกว่าอัลกอริธึม FIFO เพราะ SJF นั้นเหมาะสมกว่าเพราะช่วยลดเวลารอโดยเฉลี่ยซึ่งจะช่วยเพิ่มปริมาณงาน
อัลกอริธึม SJF เป็นแบบยึดเอาเสียก่อนและไม่ยึดเอาเสียก่อน การจัดกำหนดการชั่วคราวเรียกอีกอย่างว่า สั้นที่สุด-เหลือ-เวลา-ก่อน การตั้งเวลา ในแนวทางเชิงยึดเอาเสียก่อน กระบวนการใหม่จะเกิดขึ้นเมื่อมีกระบวนการดำเนินการอยู่แล้ว หากการแตกของกระบวนการที่มาถึงใหม่น้อยกว่าเวลาที่ระเบิดของกระบวนการดำเนินการกว่าตัวจัดกำหนดการจะแทนที่การประมวลผลของกระบวนการด้วยเวลาที่ต่อเนื่องน้อยกว่า
เวลาตอบสนอง เวลารอ และเวลาที่เสร็จสิ้นคืออะไร
- เวลาที่เสร็จสมบูรณ์ คือเวลาที่กระบวนการต้องใช้เพื่อให้การดำเนินการเสร็จสิ้น
-
เวลาตอบสนอง คือช่วงเวลาระหว่างการส่งกระบวนการและเสร็จสิ้น
เวลาดำเนินการ =เสร็จสิ้นกระบวนการ – การส่งกระบวนการ
-
เวลารอคอย คือความแตกต่างระหว่างเวลาตอบสนองกับเวลาที่ระเบิด
เวลารอ =เวลาตอบสนอง – เวลาที่ระเบิด
ตัวอย่าง
เราได้รับกับกระบวนการ P1, P2, P3, P4 และ P5 ที่มีเวลาระเบิดที่สอดคล้องกันด้านล่าง
| กระบวนการ | เวลาระเบิด | เวลาที่มาถึง |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | 4 | 0 |
| P2 | 2 | 1 |
| P3 | 8 | 2 |
| P4 | 1 | 3 |
| P5 | 9 | 4 |
เนื่องจากเวลาที่มาถึงของ P1 เป็น 0 จึงจะเป็นคนแรกที่ถูกดำเนินการจนกว่าจะถึงกระบวนการอื่น เมื่ออยู่ที่ 1 กระบวนการ P2 เข้ามา และเวลาระเบิดของ P2 นั้นน้อยกว่าเวลาที่ระเบิดของ P1 ดังนั้นตัวจัดกำหนดการจะส่ง CPU ไปพร้อมกับกระบวนการ P2 เป็นต้น
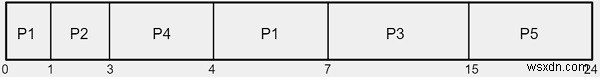
เวลารอเฉลี่ยคำนวณโดยใช้แผนภูมิแกนต์ P1 ต้องรอ (0+4)4, P2 ต้องรอ 1, P3 ต้องรอ 7, P4 ต้องรอ 3 และ P5 ต้องรอ 15. ดังนั้น เวลารอเฉลี่ยจะเท่ากับ −
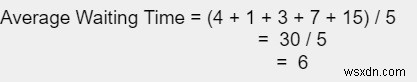
อัลกอริทึม
Start
Step 1-> Declare a struct Process
Declare pid, bt, art
Step 2-> In function findTurnAroundTime(Process proc[], int n, int wt[], int tat[])
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
Set tat[i] = proc[i].bt + wt[i]
Step 3-> In function findWaitingTime(Process proc[], int n, int wt[])
Declare rt[n]
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
Set rt[i] = proc[i].bt
Set complete = 0, t = 0, minm = INT_MAX
Set shortest = 0, finish_time
Set bool check = false
Loop While (complete != n)
Loop For j = 0 and j < n and j++
If (proc[j].art <= t) && (rt[j] < minm) && rt[j] > 0 then,
Set minm = rt[j]
Set shortest = j
Set check = true
If check == false then,
Increment t by 1
Continue
Decrement the value of rt[shortest] by 1
Set minm = rt[shortest]
If minm == 0 then,
Set minm = INT_MAX
If rt[shortest] == 0 then,
Increment complete by 1
Set check = false
Set finish_time = t + 1
Set wt[shortest] = finish_time - proc[shortest].bt -proc[shortest].art
If wt[shortest] < 0
Set wt[shortest] = 0
Increment t by 1
Step 4-> In function findavgTime(Process proc[], int n)
Declare and set wt[n], tat[n], total_wt = 0, total_tat = 0
Call findWaitingTime(proc, n, wt)
Call findTurnAroundTime(proc, n, wt, tat)
Loop For i = 0 and i < n and i++
Set total_wt = total_wt + wt[i]
Set total_tat = total_tat + tat[i]
Print proc[i].pid, proc[i].bt, wt[i], tat[i]
Print Average waiting time i.e., total_wt / n
Print Average turn around time i.e., total_tat / n
Step 5-> In function int main()
Declare and set Process proc[] = { { 1, 5, 1 }, { 2, 3, 1 }, { 3, 6, 2 }, { 4, 5, 3 } }
Set n = sizeof(proc) / sizeof(proc[0])
Call findavgTime(proc, n)
Stop ตัวอย่าง
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//structure for every process
struct Process {
int pid; // Process ID
int bt; // Burst Time
int art; // Arrival Time
};
void findTurnAroundTime(Process proc[], int n, int wt[], int tat[]) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
tat[i] = proc[i].bt + wt[i];
}
//waiting time of all process
void findWaitingTime(Process proc[], int n, int wt[]) {
int rt[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
rt[i] = proc[i].bt;
int complete = 0, t = 0, minm = INT_MAX;
int shortest = 0, finish_time;
bool check = false;
while (complete != n) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if ((proc[j].art <= t) && (rt[j] < minm) && rt[j] > 0) {
minm = rt[j];
shortest = j;
check = true;
}
}
if (check == false) {
t++;
continue;
}
// decrementing the remaining time
rt[shortest]--;
minm = rt[shortest];
if (minm == 0)
minm = INT_MAX;
// If a process gets completely
// executed
if (rt[shortest] == 0) {
complete++;
check = false;
finish_time = t + 1;
// Calculate waiting time
wt[shortest] = finish_time -
proc[shortest].bt -
proc[shortest].art;
if (wt[shortest] < 0)
wt[shortest] = 0;
}
// Increment time
t++;
}
}
// Function to calculate average time
void findavgTime(Process proc[], int n) {
int wt[n], tat[n], total_wt = 0,
total_tat = 0;
// Function to find waiting time of all
// processes
findWaitingTime(proc, n, wt);
// Function to find turn around time for
// all processes
findTurnAroundTime(proc, n, wt, tat);
cout << "Processes " << " Burst time " << " Waiting time " << " Turn around time\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
total_wt = total_wt + wt[i];
total_tat = total_tat + tat[i];
cout << " " << proc[i].pid << "\t\t" << proc[i].bt << "\t\t " << wt[i] << "\t\t " << tat[i] << endl;
}
cout << "\nAverage waiting time = " << (float)total_wt / (float)n; cout << "\nAverage turn around time = " << (float)total_tat / (float)n;
}
// main function
int main() {
Process proc[] = { { 1, 5, 1 }, { 2, 3, 1 }, { 3, 6, 2 }, { 4, 5, 3 } };
int n = sizeof(proc) / sizeof(proc[0]);
findavgTime(proc, n);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์