เส้นทางออยเลอร์เป็นเส้นทาง โดยที่เราสามารถเยี่ยมชมทุกโหนดได้เพียงครั้งเดียว เราสามารถใช้ขอบเดียวกันได้หลายครั้ง วงจรออยเลอร์เป็นเส้นทางออยเลอร์ชนิดพิเศษ เมื่อจุดยอดเริ่มต้นของเส้นทางออยเลอร์เชื่อมโยงกับจุดยอดสิ้นสุดของเส้นทางนั้นด้วย
ในการตรวจจับเส้นทางออยเลอร์ เราต้องปฏิบัติตามเงื่อนไขเหล่านี้
- ต้องเชื่อมต่อกราฟ
- เมื่อไม่มีจุดยอดของกราฟที่ไม่มีทิศทางมีดีกรีเป็นคี่ ก็จะเป็นวงจรออยเลอร์ ซึ่งเป็นเส้นทางออยเลอร์เส้นทางเดียว
- เมื่อจุดยอดสองจุดมีดีกรีเป็นคี่ มันคือเส้นทางออยเลอร์
อินพุต
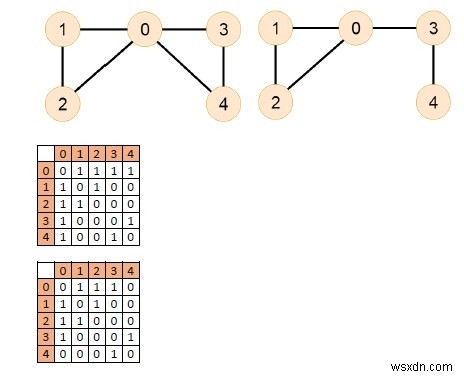
ผลลัพธ์
กราฟทั้งสองมีเส้นทางออยเลอร์
อัลกอริทึม
สำรวจ (u เยี่ยมชม)
อินพุต :โหนดเริ่มต้น u และโหนดที่เข้าชมเพื่อทำเครื่องหมายว่าโหนดใดถูกเยี่ยมชม
เอาท์พุต :ข้ามจุดยอดที่เชื่อมต่อทั้งหมด
Begin mark u as visited for all vertex v, if it is adjacent with u, do if v is not visited, then traverse(v, visited) done End
isConnected(กราฟ)
Input :กราฟ
เอาต์พุต :เป็นจริงหากเชื่อมต่อกราฟ
Begin define visited array for all vertices u in the graph, do make all nodes unvisited traverse(u, visited) if any unvisited node is still remaining, then return false done return true End
isEulerian(กราฟ)
อินพุต :กราฟที่กำหนด
เอาต์พุต :ส่งคืนค่า 1 เมื่อวงจรหรือเส้นทางออยเลอร์ และคืนค่า 0 เมื่อไม่มีเส้นทางออยเลอร์
Begin if isConnected() is false, then return false define list of degree for each node oddDegree := 0 for all vertex i in the graph, do for all vertex j which are connected with i, do increase degree done if degree of vertex i is odd, then increase oddDegree done if oddDegree > 0, then return 0 else return 1 End
โค้ดตัวอย่าง
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#define NODE 5
using namespace std;
int graph[NODE][NODE] = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0}};
/*int graph[NODE][NODE] = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 0}};*/ //uncomment to check Euler Circuit as well as path
/*int graph[NODE][NODE] = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0}};*/ //Uncomment to check Non Eulerian Graph
void traverse(int u, bool visited[]) {
visited[u] = true; //mark v as visited
for(int v = 0; v<NODE; v++) {
if(graph[u][v]) {
if(!visited[v])
traverse(v, visited);
}
}
}
bool isConnected() {
bool *vis = new bool[NODE];
//for all vertex u as start point, check whether all nodes are visible or not
for(int u; u < NODE; u++) {
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++)
vis[i] = false; //initialize as no node is visited
traverse(u, vis);
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++){
if(!vis[i]) //if there is a node, not visited by traversal, graph is not connected
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int isEulerian() {
if(isConnected() == false) //when graph is not connected
return 0;
vector<int> degree(NODE, 0);
int oddDegree = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j<NODE; j++) {
if(graph[i][j])
degree[i]++; //increase degree, when connected edge found
}
if(degree[i] % 2 != 0) //when degree of vertices are odd
oddDegree++; //count odd degree vertices
}
if(oddDegree > 2) //when vertices with odd degree greater than 2
return 0;
return 1; //when oddDegree is 0, it is Euler circuit, and when 2, it is Euler path
}
int main() {
if(isEulerian() != 0) {
cout << "The graph has Eulerian path." << endl;
} else {
cout << "The graph has No Eulerian path." << endl;
}
} ผลลัพธ์
The graph has Eulerian path.


