เราได้รับข้อมูลและลำดับความสำคัญเป็นค่าจำนวนเต็ม และภารกิจคือการสร้างรายการที่เชื่อมโยงตามลำดับความสำคัญที่กำหนดและแสดงผล
คิวเป็นโครงสร้างข้อมูล FIFO โดยองค์ประกอบที่แทรกก่อนเป็นองค์ประกอบแรกที่จะถูกลบออก คิวลำดับความสำคัญเป็นประเภทของคิวที่สามารถแทรกหรือลบองค์ประกอบขึ้นอยู่กับลำดับความสำคัญ สามารถใช้งานได้โดยใช้โครงสร้างข้อมูลคิว สแต็ก หรือรายการลิงก์ คิวลำดับความสำคัญจะดำเนินการตามกฎเหล่านี้ -
- ข้อมูลหรือองค์ประกอบที่มีลำดับความสำคัญสูงสุดจะถูกดำเนินการก่อนข้อมูลหรือองค์ประกอบที่มีลำดับความสำคัญต่ำสุด
- หากองค์ประกอบสองรายการมีลำดับความสำคัญเท่ากันกว่าองค์ประกอบนั้นจะถูกดำเนินการตามลำดับ องค์ประกอบนั้นจะถูกเพิ่มในรายการ
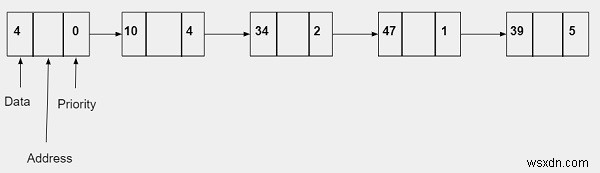
โหนดของรายการที่เชื่อมโยงสำหรับการนำคิวลำดับความสำคัญไปใช้จะมีสามส่วน -
- ข้อมูล − จะเก็บค่าจำนวนเต็ม
- ที่อยู่ − มันจะเก็บที่อยู่ของโหนดถัดไป
- ลำดับความสำคัญ −มันจะเก็บลำดับความสำคัญซึ่งเป็นค่าจำนวนเต็ม สามารถอยู่ในช่วงตั้งแต่ 0-10 โดยที่ 0 หมายถึงลำดับความสำคัญสูงสุด และ 10 หมายถึงลำดับความสำคัญต่ำสุด
ตัวอย่าง
ป้อนข้อมูล
ผลผลิต

อัลกอริทึม
Start Step 1-> Declare a struct node Declare data, priority Declare a struct node* next Step 2-> In function Node* newNode(int d, int p) Set Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)) Set temp->data = d Set temp->priority = p Set temp->next = NULL Return temp Step 3-> In function int peek(Node** head) return (*head)->data Step 4-> In function void pop(Node** head) Set Node* temp = *head Set (*head) = (*head)->next free(temp) Step 5-> In function push(Node** head, int d, int p) Set Node* start = (*head) Set Node* temp = newNode(d, p) If (*head)->priority > p then, Set temp->next = *head Set (*head) = temp Else Loop While start->next != NULL && start->next->priority < p Set start = start->next Set temp->next = start->next Set start->next = temp Step 6-> In function int isEmpty(Node** head) Return (*head) == NULL Step 7-> In function int main() Set Node* pq = newNode(7, 1) Call function push(&pq, 1, 2) Call function push(&pq, 3, 3) Call function push(&pq, 2, 0) Loop While (!isEmpty(&pq)) Print the results obtained from peek(&pq) Call function pop(&pq) Stop
ตัวอย่าง
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// priority Node
typedef struct node {
int data;
int priority;
struct node* next;
} Node;
Node* newNode(int d, int p) {
Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
temp->data = d;
temp->priority = p;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
int peek(Node** head) {
return (*head)->data;
}
void pop(Node** head) {
Node* temp = *head;
(*head) = (*head)->next;
free(temp);
}
void push(Node** head, int d, int p) {
Node* start = (*head);
Node* temp = newNode(d, p);
if ((*head)->priority > p) {
temp->next = *head;
(*head) = temp;
} else {
while (start->next != NULL &&
start->next->priority < p) {
start = start->next;
}
// Either at the ends of the list
// or at required position
temp->next = start->next;
start->next = temp;
}
}
// Function to check the queue is empty
int isEmpty(Node** head) {
return (*head) == NULL;
}
// main function
int main() {
Node* pq = newNode(7, 1);
push(&pq, 1, 2);
push(&pq, 3, 3);
push(&pq, 2, 0);
while (!isEmpty(&pq)) {
printf("%d ", peek(&pq));
pop(&pq);
}
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
2 7 1 3


