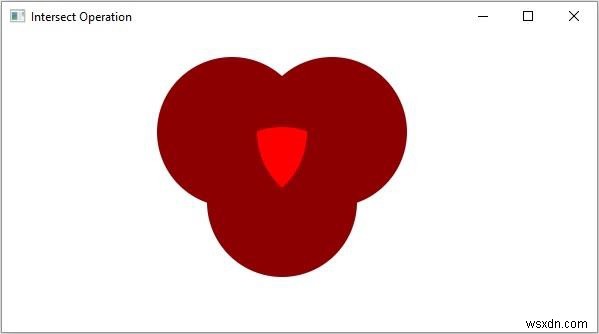
การดำเนินการนี้ใช้รูปร่างตั้งแต่สองรูปร่างขึ้นไปเป็นอินพุตและส่งกลับพื้นที่ทางแยกระหว่างรูปร่างดังที่แสดงด้านล่าง
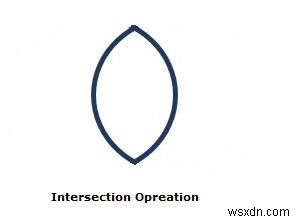
จุดตัด() (คงที่) เมธอดของคลาส javafx.scene.shape.Shape ยอมรับออบเจ็กต์ Shape สองออบเจ็กต์และส่งคืนผลลัพธ์ของการดำเนินการตัดกันของออบเจ็กต์ที่กำหนด
ตัวอย่าง
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.scene.shape.Shape;
public class JavaFXIntersectExample extends Application {
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Drawing circle1
Circle circle1 = new Circle();
circle1.setCenterX(230.0f);
circle1.setCenterY(100.0f);
circle1.setRadius(75.0f);
circle1.setFill(Color.DARKRED);
//Drawing Circle2
Circle circle2 = new Circle();
circle2.setCenterX(280.0f);
circle2.setCenterY(170.0f);
circle2.setRadius(75.0f);
circle2.setFill(Color.DARKRED);
//Drawing Circle3
Circle circle3 = new Circle();
circle3.setCenterX(330.0f);
circle3.setCenterY(100.0f);
circle3.setRadius(75.0f);
circle3.setFill(Color.DARKRED);
//Intersect Operation
Shape intersect = Shape.intersect(circle1, circle2);
intersect = Shape.intersect(intersect, circle3);
intersect.setFill(Color.RED);
//Setting the stage
Group root = new Group(circle1, circle2, circle3, intersect);
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 595, 300);
stage.setTitle("Intersect Operation");
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
} ผลลัพธ์