ที่นี่เราจะเห็นโครงสร้างข้อมูลต้นไม้ไบนารีแบบเธรด เรารู้ว่าโหนดไบนารีอาจมีลูกได้มากที่สุดสองคน แต่ถ้าพวกเขามีลูกเพียงคนเดียว หรือไม่มีลูก ส่วนลิงก์ในการแสดงรายการลิงก์ยังคงเป็นโมฆะ ด้วยการใช้การแสดงไบนารีทรีแบบเธรด เราสามารถใช้ลิงก์ว่างนั้นซ้ำได้โดยการสร้างเธรดบางอัน
หากโหนดหนึ่งมีพื้นที่ชายน์ว่างด้านซ้ายหรือขวา โหนดนั้นจะถูกใช้เป็นเธรด ทรีไบนารีแบบเธรดมีสองประเภท ต้นไม้แบบเกลียวเดียวหรือแบบไบนารีที่มีเกลียวเต็ม
สำหรับไบนารีทรีแบบเธรดทั้งหมด แต่ละโหนดมีห้าฟิลด์ สามฟิลด์เช่นโหนดไบนารีปกติ อีกสองฟิลด์สำหรับเก็บค่าบูลีนเพื่อระบุว่าลิงค์ของด้านนั้นเป็นลิงค์หรือเธรดจริงหรือไม่
| แฟล็กเธรดด้านซ้าย | ลิงก์ซ้าย | ข้อมูล | ลิงก์ขวา | แฟล็กเธรดด้านขวา |
นี่คือไบนารีทรีแบบเธรดแบบเต็ม
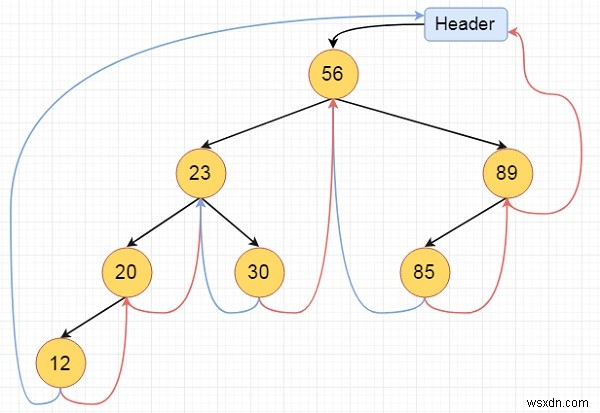
อัลกอริทึม
inorder(): Begin temp := root repeat infinitely, do p := temp temp = right of temp if right flag of p is false, then while left flag of temp is not null, do temp := left of temp done end if if temp and root are same, then break end if print key of temp done End
ตัวอย่าง
#include <iostream>
#define MAX_VALUE 65536
using namespace std;
class N { //node declaration
public:
int k;
N *l, *r;
bool leftTh, rightTh;
};
class ThreadedBinaryTree {
private:
N *root;
public:
ThreadedBinaryTree() { //constructor to initialize the variables
root= new N();
root->r= root->l= root;
root->leftTh = true;
root->k = MAX_VALUE;
}
void insert(int key) {
N *p = root;
for (;;) {
if (p->k< key) { //move to right thread
if (p->rightTh)
break;
p = p->r;
}
else if (p->k > key) { // move to left thread
if (p->leftTh)
break;
p = p->l;
}
else {
return;
}
}
N *temp = new N();
temp->k = key;
temp->rightTh= temp->leftTh= true;
if (p->k < key) {
temp->r = p->r;
temp->l= p;
p->r = temp;
p->rightTh= false;
}
else {
temp->r = p;
temp->l = p->l;
p->l = temp;
p->leftTh = false;
}
}
void inorder() { //print the tree
N *temp = root, *p;
for (;;) {
p = temp;
temp = temp->r;
if (!p->rightTh) {
while (!temp->leftTh) {
temp = temp->l;
}
}
if (temp == root)
break;
cout<<temp->k<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
};
int main() {
ThreadedBinaryTree tbt;
cout<<"Threaded Binary Tree\n";
tbt.insert(56);
tbt.insert(23);
tbt.insert(89);
tbt.insert(85);
tbt.insert(20);
tbt.insert(30);
tbt.insert(12);
tbt.inorder();
cout<<"\n";
} ผลลัพธ์
Threaded Binary Tree 12 20 23 30 56 85 89


