ในปัญหานี้ เราได้รับกราฟกำกับ และเราต้องพิมพ์เส้นทางทั้งหมดจากต้นทางไปยังปลายทางของกราฟ
กราฟกำกับ เป็นกราฟที่มีขอบที่ชี้จากจุดยอด a ถึง b
มาดูตัวอย่างทำความเข้าใจปัญหากัน
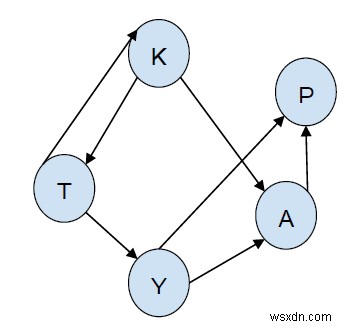
ต้นทาง =K ปลายทาง =P
ผลลัพธ์:
K -> T -> Y -> A -> P K -> T -> Y -> P K -> A -> P
ที่นี่เราพบเส้นทางจาก K ถึง P เราได้สำรวจเส้นทางและพิมพ์เส้นทางทั้งหมดจาก K ที่นำเราไปยัง P.
เพื่อแก้ปัญหานี้ เราจะสำรวจกราฟโดยใช้การค้นหาเชิงลึกก่อน เทคนิคการข้ามผ่าน เริ่มจากต้นทาง เราจะสำรวจแต่ละร้านค้าจุดยอดในอาร์เรย์เส้นทางของเราและทำเครื่องหมายว่าเยี่ยมชมแล้ว (เพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงการเยี่ยมชมจุดสุดยอดเดียวกันหลายครั้ง) และพิมพ์เส้นทางนี้เมื่อ ปลายทาง ถึงจุดสุดยอดแล้ว
มาดูโปรแกรมนำตรรกะไปใช้กัน -
ตัวอย่าง
#include<iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
class Graph {
int V;
list<int> *adj;
void findNewPath(int , int , bool [], int [], int &);
public:
Graph(int V);
void addEdge(int u, int v);
void printPaths(int s, int d);
};
Graph::Graph(int V) {
this->V = V;
adj = new list<int>[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v) {
adj[u].push_back(v);
}
void Graph::printPaths(int s, int d) {
bool *visited = new bool[V];
int *path = new int[V];
int path_index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
findNewPath(s, d, visited, path, path_index);
}
void Graph::findNewPath(int u, int d, bool visited[],
int path[], int &path_index) {
visited[u] = true;
path[path_index] = u;
path_index++;
if (u == d) {
for (int i = 0; i<path_index; i++)
cout<<path[i]<<" ";
cout << endl;
} else {
list<int>::iterator i;
for (i = adj[u].begin(); i != adj[u].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
findNewPath(*i, d, visited, path, path_index);
}
path_index--;
visited[u] = false;
}
int main() {
Graph g(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(1, 3);
int s = 2, d = 3;
cout<<"Following are all different paths from source to destination : \n";
g.printPaths(s, d);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
Following are all different paths from source to destination : 2 0 1 3 2 0 3 2 1 3


