พิจารณาว่าเรามีต้นไม้ไบนารี เราต้องค้นหาว่ามีต้นไม้ย่อยที่ซ้ำกันที่มีขนาด 2 หรือมากกว่าในต้นไม้หรือไม่ สมมติว่าเรามีไบนารีทรีด้านล่าง -
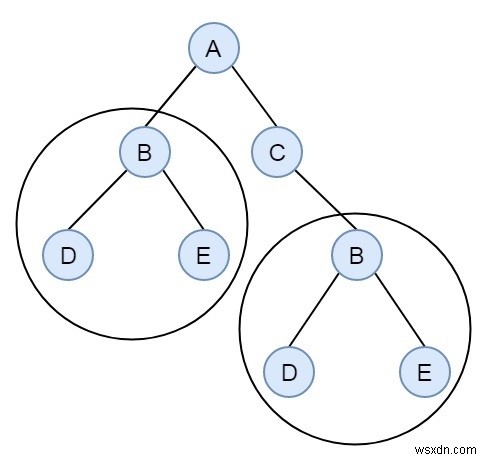
มีแผนผังย่อยที่มีขนาด 2 เหมือนกันสองต้น เราสามารถแก้ปัญหานี้ได้โดยใช้การทำให้เป็นอนุกรมของต้นไม้และกระบวนการแฮช แนวคิดกำลังทำให้ทรีย่อยเป็นอนุกรมเป็นสตริง และจัดเก็บไว้ในตารางแฮช เมื่อเราพบต้นไม้ที่ต่อเนื่องกันซึ่งไม่ใช่ใบไม้ มีอยู่แล้วในตารางแฮช จากนั้นคืนค่าจริง
ตัวอย่าง
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
const char MARKER = '$';
struct Node {
public:
char key;
Node *left, *right;
};
Node* getNode(char key) {
Node* newNode = new Node;
newNode->key = key;
newNode->left = newNode->right = NULL;
return newNode;
}
unordered_set<string> subtrees;
string duplicateSubtreeFind(Node *root) {
string res = "";
if (root == NULL) // If the current node is NULL, return $
return res + MARKER;
string l_Str = duplicateSubtreeFind(root->left);
if (l_Str.compare(res) == 0)
return res;
string r_Str = duplicateSubtreeFind(root->right);
if (r_Str.compare(res) == 0)
return res;
res = res + root->key + l_Str + r_Str;
if (res.length() > 3 && subtrees.find(res) != subtrees.end()) //if subtree is present, then return blank string return "";
subtrees.insert(res);
return res;
}
int main() {
Node *root = getNode('A');
root->left = getNode('B');
root->right = getNode('C');
root->left->left = getNode('D');
root->left->right = getNode('E');
root->right->right = getNode('B');
root->right->right->right = getNode('E');
root->right->right->left= getNode('D');
string str = duplicateSubtreeFind(root);
if(str.compare("") == 0)
cout << "It has dublicate subtrees of size more than 1";
else
cout << "It has no dublicate subtrees of size more than 1" ;
} ผลลัพธ์
It has dublicate subtrees of size more than 1


