ให้เมทริกซ์ M[r][c], 'r' หมายถึงจำนวนแถวและ 'c' หมายถึงจำนวนคอลัมน์ที่ r =c สร้างเมทริกซ์สี่เหลี่ยมจัตุรัส เราต้องหาว่าเมทริกซ์สี่เหลี่ยมจัตุรัสที่กำหนดเป็น แนวทแยง . หรือไม่ และ สเกลาร์ เมทริกซ์หรือไม่ถ้าเป็น แนวทแยง และ สเกลาร์ เมทริกซ์แล้วพิมพ์ใช่ในผลลัพธ์
เมทริกซ์แนวทแยง
เมทริกซ์สี่เหลี่ยมจัตุรัส m[][] จะเป็นเมทริกซ์แนวทแยงก็ต่อเมื่อองค์ประกอบยกเว้นเส้นทแยงมุมหลักเป็นศูนย์
ดังรูปด้านล่าง −
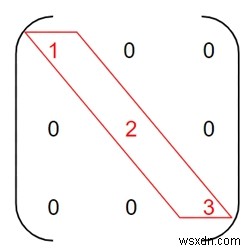
ในที่นี้ องค์ประกอบในสีแดงคือเส้นทแยงมุมหลัก ซึ่งเป็นองค์ประกอบที่พักที่ไม่เป็นศูนย์ ยกเว้นเส้นทแยงมุมหลักเป็นศูนย์ ทำให้เป็น เมทริกซ์แนวทแยง .
ตัวอย่าง
Input: m[3][3] = { {7, 0, 0},
{0, 8, 0},
{0, 0, 9}}
Output: yes
Input: m[3][3] = { {1, 2, 3},
{0, 4, 0},
{0, 0, 5}
}
Output: no อัลกอริทึม
Start
Step 1 -> define macro of size 4
Step 2 -> declare function to check if matrix is diagonal or not
bool ifdiagonal(int arr[size][size])
Loop For int i = 0 and i < size and i++
Loop for int j = 0 and j < size and j++
IF ((i != j) & (arr[i][j] != 0))
return false
End
End
End
return true
step 3 -> In main()
Declare and set int arr[size][size] = { { 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 1 }
};
IF (ifdiagonal(arr))
Print its a diagonal matrix
End
Else
Print its not a diagonal matrix
End
Stop เมทริกซ์แนวทแยง
ตัวอย่าง
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define size 4
using namespace std;
// check if matrix is diagonal matrix or not.
bool ifdiagonal(int arr[size][size]){
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++)
if ((i != j) && (arr[i][j] != 0))
return false;
return true;
}
int main(){
int arr[size][size] = { { 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 1 }
};
if (ifdiagonal(arr))
cout << "its a diagonal matrix" << endl;
else
cout << "its not a diagonal matrix" << endl;
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
its a diagonal matrix
สเกลาร์เมทริกซ์
เมทริกซ์กำลังสอง m[][] คือ เมทริกซ์สเกลาร์ หากองค์ประกอบในแนวทแยงหลักเท่ากันและองค์ประกอบที่เหลือเป็นศูนย์
ดังตัวอย่างด้านล่าง −
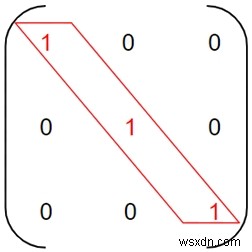
ในที่นี้ องค์ประกอบในสีแดงคือองค์ประกอบในแนวทแยงที่เหมือนกัน และองค์ประกอบที่เหลือเป็นศูนย์ ทำให้เป็น เมทริกซ์สเกลาร์ .
ตัวอย่าง
Input: m[3][3] = { {2, 0, 0},
{0, 2, 0},
{0, 0, 2} }
Output: yes
Input: m[3][3] = { {3, 0, 0},
{0, 2, 0},
{0, 0, 3} }
Output: no อัลกอริทึม
Start
Step 1 -> Declare macro as #define size 4
Step 2 -> declare function to check matrix is scalar matrix or not.
bool scalar(int arr[size][size])
Loop For int i = 0 and i < size and i++
Loop For int j = 0 and j < size and j++
IF ((i != j) && (arr[i][j] != 0))
return false
End
End
End
Loop for int i = 0 and i < size – 1 and i++
If (arr[i][i] != arr[i + 1][i + 1])
return false
End
End
Return true
Step 3 -> In main()
Declare array as int arr[size][size] = { { 2, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 2, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 2, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 2 }
}
IF(scalar(arr))
Print its a scalar matrix
Else
Print its not a scalar matrix
Stop ตัวอย่าง
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define size 4
using namespace std;
// check matrix is scalar matrix or not.
bool scalar(int arr[size][size]){
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++)
if ((i != j) && (arr[i][j] != 0))
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++)
if (arr[i][i] != arr[i + 1][i + 1])
return false;
return true;
}
int main(){
int arr[size][size] = { { 2, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 2, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 2, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 2 } };
if (scalar(arr))
cout << "its a scalar matrix" << endl;
else
cout << "its not a scalar matrix" << endl;
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
its a scalar matrix


