สำหรับการสร้างจุดข้อมูลใหม่ภายในช่วงของชุดข้อมูลที่กำหนดแบบไม่ต่อเนื่อง จะใช้เทคนิคการประมาณค่า เทคนิคการสอดแทรก Lagrange เป็นหนึ่งในนั้น เมื่อจุดข้อมูลที่กำหนดไม่มีการกระจายอย่างเท่าเทียมกัน เราสามารถใช้วิธีการแก้ไขนี้เพื่อค้นหาวิธีแก้ปัญหา สำหรับการแก้ไข Lagrange เราต้องทำตามสมการนี้
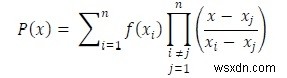
อินพุตและเอาต์พุต
Input:
List of x and f(x) values. find f(3.25)
x: {0,1,2,3,4,5,6}
f(x): {0,1,8,27,64,125,216}
Output:
Result after Lagrange interpolation f(3.25) = 34.3281 อัลกอริทึม
largrangeInterpolation(x: array, fx: array, x1)
ป้อนข้อมูล - x array และ fx array สำหรับรับข้อมูลที่ทราบก่อนหน้านี้ และชี้ x1
ผลลัพธ์: ค่าของ f(x1).
Begin res := 0 and tempSum := 0 for i := 1 to n, do tempProd := 1 for j := 1 to n, do if i ≠ j, then tempProf := tempProd * (x1 – x[j])/(x[i] – x[j]) done tempPord := tempProd * fx[i] res := res + tempProd done return res End
ตัวอย่าง
#include<iostream>
#define N 6
using namespace std;
double lagrange(double x[], double fx[], double x1) {
double res = 0, tempSum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i<=N; i++) {
double tempProd = 1; //for each iteration initialize temp product
for(int j = 1; j<=N; j++) {
if(i != j) { //if i = j, then denominator will be 0
tempProd *= (x1 - x[j])/(x[i] - x[j]); //multiply each term using formula
}
}
tempProd *= fx[i]; //multiply f(xi)
res += tempProd;
}
return res;
}
main() {
double x[N+1] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6};
double y[N+1] = {0,1,8,27,64,125,216};
double x1 = 3.25;
cout << "Result after lagrange interpolation f("<<x1<<") = " << lagrange(x, y, x1);
} ผลลัพธ์
Result after lagrange interpolation f(3.25) = 34.3281


