โพสต์นี้จะแนะนำ PostgreSQL และแนะนำคุณเกี่ยวกับการติดตั้งและการกำหนดค่าเวอร์ชัน 9.3 บน Linux®
แนะนำตัว
PostgreSQL คือระบบจัดการฐานข้อมูลเชิงสัมพันธ์แบบโอเพนซอร์ส (RDBMS) ที่ล้ำหน้าที่สุดในโลก องค์กรชั้นนำมากมาย เช่น Apple, IMDB, Skype, Uber, Lockheed Martin, Verizon และอื่นๆ ใช้ PostgreSQL RDBMS นี้เริ่มต้นในปี 1986 โดยเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของโครงการ POSTGRES ที่มหาวิทยาลัยแห่งแคลิฟอร์เนียที่เบิร์กลีย์ และมีการพัฒนาอย่างต่อเนื่องมากกว่า 30 ปีบนแพลตฟอร์มหลัก
PostgreSQL ทำงานบนระบบปฏิบัติการหลักทั้งหมดและเป็นไปตามข้อกำหนดของ ACID ตั้งแต่ปี 2544 ตัวย่อ ACID ประกอบด้วยองค์ประกอบต่อไปนี้:
- ปรมาณู :คุณรับประกันว่าธุรกรรมทั้งหมดจะสำเร็จหรือไม่ก็ตาม
- ความสม่ำเสมอ :คุณรับประกันว่าข้อมูลทั้งหมดสอดคล้องกัน ข้อมูลทั้งหมดถูกต้องตามกฎที่กำหนดไว้ กฎรวมถึงข้อจำกัด การเรียงซ้อน และทริกเกอร์ที่ใช้กับฐานข้อมูล
- ความโดดเดี่ยว :ธุรกรรมทั้งหมดเกิดขึ้นแยกกัน ธุรกรรมนี้ไม่สามารถอ่านข้อมูลจากธุรกรรมอื่นที่ยังไม่เสร็จสิ้นได้
- ความทนทาน :หลังจากที่คุณทำธุรกรรม รายการนั้นจะยังคงอยู่ในระบบ แม้ว่าระบบจะขัดข้องทันทีหลังการดำเนินการ
ไม่น่าแปลกใจเลยที่ PostgreSQL ทำหน้าที่เป็นฐานข้อมูลเชิงสัมพันธ์แบบโอเพนซอร์สสำหรับคนและองค์กรจำนวนมาก เนื่องจากมีส่วนเสริมที่ทรงพลัง เช่น ตัวขยายฐานข้อมูลเชิงพื้นที่ของ PostGIS ยอดนิยม
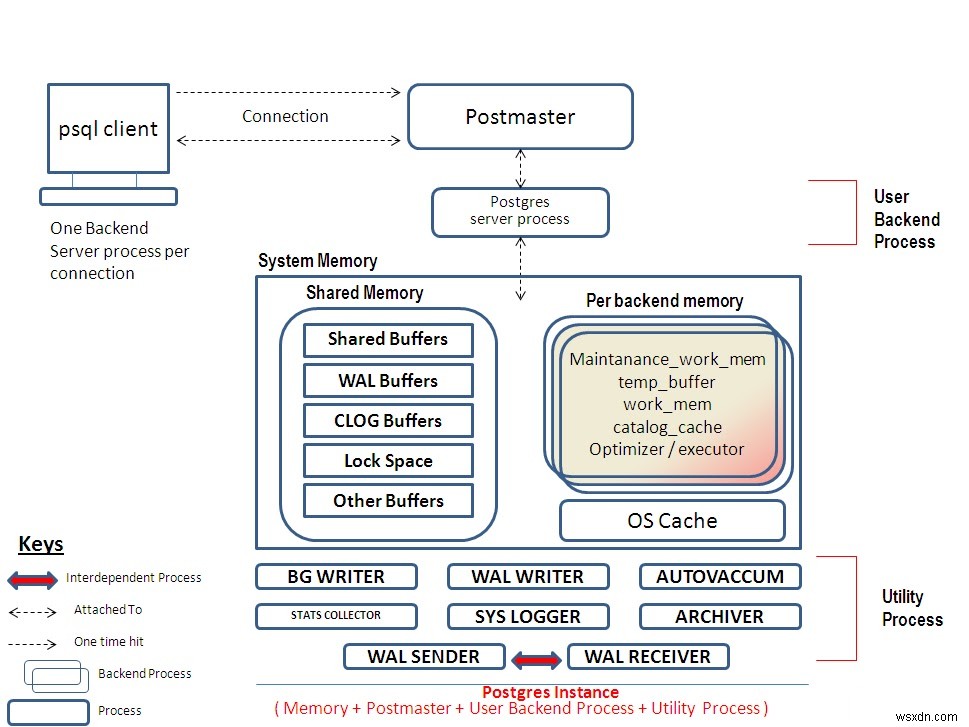
ที่มาของภาพ :https://postgresql-database.blogspot.com/2013/08/postgresql-architecture.html
สนับสนุน
SLA การสนับสนุนด้านการผลิตมีให้จากบริษัทต่อไปนี้:
- https://www.enterprisedb.com
- https://www.2ndquadrant.com/
- https://www.revsys.com/
- https://imperoit.com/PostgreSQL_Support.htm
รุ่นที่รองรับ:ปัจจุบัน (12) / 11 / 10 / 9.6 / 9.5 / 9.4 รุ่นพัฒนา:devel รุ่นที่ไม่รองรับ:9.3 / 9.2 / 9.1 / 9.0 / 8.4 / 8.3 / 8.2
การติดตั้งและการกำหนดค่า
ทำตามขั้นตอนต่อไปนี้เพื่อติดตั้งและกำหนดค่า Postgres 9.3:
ติดตั้ง Postgres 9.3 บน Linux 7.1
รันคำสั่งต่อไปนี้เพื่อติดตั้ง Postgres 9.3 บน Red Hat® Linux 7.1:
[root@snwdbsolpeprod01 ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 7.1 (Maipo)
สร้างโฟลเดอร์ว่าง
สร้างโฟลเดอร์ว่างสำหรับการติดตั้งฐานข้อมูล
[root@snwdbsolpeprod01 mnt]# mkdir postt
[root@snwdbsolpeprod01 postt]# pwd
/mnt/postt
ดาวน์โหลด RPM
เรียกใช้คำสั่งต่อไปนี้เพื่อดาวน์โหลด Red Hat Package Manager (RPM) สำหรับเวอร์ชัน OS ของคุณเพื่อเริ่มการติดตั้ง Postgres:
[root@snwdbsolpeprod01 postt]# wget https://yum.postgresql.org/9.3/redhat/rhel-7-x86_64/pgdg-redhat93-9.3-2.noarch.rpm
ติดตั้ง RPM
ติดตั้งแพ็คเกจ RPM โดยใช้คำสั่งต่อไปนี้:
root@snwdbsolpeprod01 postt]# rpm -ivh pgdg-redhat93-9.3-2.noarch.rpm
ติดตั้งแพ็คเกจเพิ่มเติม
หลังจากที่คุณติดตั้ง RPM แล้ว คุณต้องติดตั้งแพ็คเกจ Postgre ที่ติดตั้งซอฟต์แวร์ DB
[root@snwdbsolpeprod01 postt]# yum install postgresql-contrib.x86_64
[root@snwdbsolpeprod01 postt]# yum install postgresql93-server.x86_64
กำหนดค่าตำแหน่ง PGDATA
กำหนดตำแหน่งที่จะจัดเก็บข้อมูล หากต้องการใช้ตำแหน่งที่ไม่ใช่ค่าเริ่มต้นสำหรับข้อมูล ให้แก้ไขบริการ PostgreSQL sysconfig และเปลี่ยนอาร์กิวเมนต์ PGDATA
vi /etc/rc.d/init.d/postgresql
vi /etc/sysconfig/pgsql/postgresql
หมายเหตุ :หาก PostgreSQL ใน sysconfig/pgsql ไม่มีอยู่ ให้สร้างและเพิ่มบรรทัดที่ระบุว่าคุณต้องการเก็บข้อมูลไว้ที่ใด ดังที่แสดงในตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้:
[root@snwdbsolpeprod01 pgsql]# cd /etc/sysconfig/pgsql/
[root@snwdbsolpeprod01 pgsql]# vi postgresql
[root@snwdbsolpeprod01 pgsql]# cat postgresql
PDGATA=/mnt/postt
เริ่มต้นฐานข้อมูล
คำสั่งแรก (จำเป็นเพียงครั้งเดียว) คือการเริ่มต้นฐานข้อมูลใน PGDATA
service <name> initdb
ตัวอย่างเช่น:สำหรับเวอร์ชัน 9.3:
service postgresql-9.3 initdb
หรือ
/usr/pgsql-9.3/bin/postgresql93-setup initdb
[root@snwdbsolpeprod01 data]# /usr/pgsql-9.3/bin/postgresql93-setup initdb
Initializing database ... OK
ตั้งค่า Postgres ให้เริ่มทำงานโดยอัตโนมัติ
หากคุณต้องการให้ PostgreSQL เริ่มทำงานโดยอัตโนมัติเมื่อระบบปฏิบัติการเริ่มทำงาน ให้ใช้คำสั่งต่อไปนี้:
[root@snwdbsolpeprod01 data]# chkconfig postgresql-9.3 on
หมายเหตุ :การส่งต่อคำขอไปที่ 'systemctl enable postgresql-9.3.service'
เริ่มบริการ PostgreSQL
ในการเริ่มบริการ PostgreSQL ให้เรียกใช้คำสั่งต่อไปนี้:
[root@snwdbsolpeprod01 data]# systemctl start postgresql-9.3.service
กำหนดค่าฐานข้อมูล
คุณสามารถกำหนดค่าฐานข้อมูลได้อย่างง่ายดายโดยอัปเดต postgresql.conf ตามที่แสดงในตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้:
vi /var/lib/pgsql/9.3/data/postgresql.conf
เปลี่ยนสิ่งต่อไปนี้:
listen_address = ‘*’
port = 15000
max_connections=300
shared_buffers = 8192MB # min 128kB
# (change requires restart)
temp_buffers = 128MB # min 800kB
max_prepared_transactions = 20 # zero disables the feature
log_destination = 'csvlog'
logging_collector = on
log_directory = '/mnt/pgsql/logs'
log_filename = 'postgresql-%a.log'
#------------------------------------------------
# AUTOVACUUM PARAMETERS
#------------------------------------------------
autovacuum = on
# Enable autovacuum subprocess? 'on'
# requires track_counts to also be on.
#log_autovacuum_min_duration = -1 # -1 disables, 0 logs all actions and
# their durations, > 0 logs only
# actions running at least this number
# of milliseconds.
autovacuum_max_workers = 3 # max number of autovacuum subprocesses
# (change requires restart)
autovacuum_naptime = 10080min # time between autovacuum runs
autovacuum_vacuum_threshold = 1000 # min number of row updates before
# vacuum
#autovacuum_analyze_threshold = 50 # min number of row updates before
# analyze
#autovacuum_vacuum_scale_factor = 0.2 # fraction of table size before vacuum
#autovacuum_analyze_scale_factor = 0.1 # fraction of table size before analyze
#autovacuum_freeze_max_age = 200000000 # maximum XID age before forced vacuum
# (change requires restart)
#autovacuum_multixact_freeze_max_age = 400000000 # maximum Multixact age
# before forced vacuum
# (change requires restart)
#autovacuum_vacuum_cost_delay = 20ms # default vacuum cost delay for
# autovacuum, in milliseconds;
# -1 means use vacuum_cost_delay
#autovacuum_vacuum_cost_limit = -1 # default vacuum cost limit for
# autovacuum, -1 means use
# vacuum_cost_limit
กำหนดการตั้งค่าการเชื่อมต่อฐานข้อมูล
ในการจำกัดหรือจัดการการตั้งค่าการเชื่อมต่อฐานข้อมูล ให้รันคำสั่งต่อไปนี้:
vi /var/lib/pgsql/9.3/data/pg_hba.conf
# TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD
# "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only
local all all peer
local all postgres md5
local all postgres ident
# IPv4 local connections:
# IPv6 local connections:
host all all ::1/128 ident
host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
# Allow replication connections from localhost, by a user with the
# replication privilege.
#local replication postgres peer
#host replication postgres 127.0.0.1/32 ident
#host replication postgres ::1/128 ident
กำหนดค่าไฟร์วอลล์
ในการกำหนดค่าพอร์ตบนไฟร์วอลล์ ให้รันคำสั่งต่อไปนี้:
iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 15000 --syn -j ACCEPT
service iptables save
service iptables restart
root@snwdbsolpeprod01 postt]# service postgresql-9.3 restart
สร้างผู้ใช้หรือบทบาท
ในการสร้างผู้ใช้หรือบทบาทใหม่ในฐานข้อมูล ให้รันคำสั่งต่อไปนี้:
su – postgres
psql -p 15000
postgres=# CREATE ROLE OCT1 LOGIN
UNENCRYPTED PASSWORD 'test@123'
INHERIT REPLICATION;
สร้างพื้นที่ตาราง
ในการสร้าง tablespace ใหม่บนฐานข้อมูล ให้รันคำสั่งต่อไปนี้:
postgres=# CREATE TABLESPACE OCT1_tablespace
OWNER ilusr
LOCATION '/usrdata/pgsql/data/oct';
สร้างฐานข้อมูล
ในการสร้างฐานข้อมูลใหม่ ให้รันคำสั่งต่อไปนี้:
postgres=# CREATE DATABASE OCT1
WITH ENCODING='UTF8'
OWNER=test
LC_CTYPE='en_US.UTF-8'
CONNECTION LIMIT=-1
TABLESPACE=OCT1_tablespace;
คำสั่งพื้นฐาน
คำสั่งการดูแลระบบพื้นฐานบางคำสั่งมีดังต่อไปนี้:
หยุดและเริ่ม PostgreSQL
/opt/PostgreSQL/9.3/bin/pg_ctl -D /mnt/postt/data stop
/opt/PostgreSQL/9.3/bin/pg_ctl -D /mnt/postt/data start
/opt/PostgreSQL/9.3/bin/pg_ctl -D /mnt/postt/data restart
/opt/PostgreSQL/9.3/bin/pg_ctl -D opt/PostgreSQL/9.4/data –m smart stop #wait for complete the transactions
/opt/PostgreSQL/9.3/bin/pg_ctl -D /mnt/postt/data –m fast stop #Immediate stop
/opt/PostgreSQL/9.3/bin/pg_ctl -D /mnt/postt/data –m immediate stop #Abort the DB
/opt/PostgreSQL/9.3/bin/pg_ctl -D /mnt/postt/data –m smart restart
/opt/PostgreSQL/9.3/bin/pg_ctl -D /mnt/postt/data –m fast restart
/opt/PostgreSQL/9.3/bin/pg_ctl -D /mnt/postt/data –m immediate restart
ตรวจสอบเวอร์ชัน PostgreSQL
postgres=# select version();
ระบุกิจกรรมในระดับฐานข้อมูลเฉพาะ
select pid,backend_xid,backend_xmin,query from pg_stat_activity ;
วิเคราะห์สถานะของตาราง
select relname,last_autoanalyze,last_analyze,n_mod_since_analyze from pg_stat_all_tables;
ค้นหาเส้นทางจริงของตาราง
postgres=# SELECT pg_relation_filepath('testpitr1');
pg_relation_filepath
----------------------
base/13003/16399
[postgres@postgres221 data]$ ls -l /mnt/postt/data/base/13003/16399
-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 256024576 Feb 21 06:36 /mnt/postt/data/base/13003/16399
รับชื่อสคีมาภายในอินสแตนซ์หรือคลัสเตอร์
select schema_name from information_schema.schemata;
select nspname from pg_catalog.pg_namespace;
post_gre=# \dn
List of schemas
Name | Owner
--------------+----------
kailash_test | postgres
public | postgres
(2 rows)
รับ dbnames ภายในอินสแตนซ์หรือคลัสเตอร์
template1=# select datname from pg_database;
template1
template0
post_gre
template1=# \l
post_gre | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =Tc/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres +
| | | | | kailash_s=CTc/postgres
template0 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | |
template1=# select usename from pg_catalog.pg_user;
kailash
kailash_s
postgres
template1=# \du
kailash | | {}
kailash_s | Superuser, Create role, Create DB | {}
postgres | Superuser, Create role, Create DB, Replication | {}
บทสรุป
แท็กไลน์ของ PostgreSQL อ้างว่าเป็น "ฐานข้อมูลโอเพ่นซอร์สที่ล้ำหน้าที่สุดในโลก" อย่างไรก็ตาม PostgreSQL ไม่ได้เป็นเพียงเชิงสัมพันธ์ แต่เป็นเชิงวัตถุ ความแตกต่างนี้ทำให้ได้เปรียบเหนือฐานข้อมูลโอเพ่นซอร์ส SQL อื่นๆ เช่น MySQL, MariaDB และ Firebird PostgreSQL เป็นตัวเลือกที่ชัดเจนบน AWScloud สำหรับการย้าย RDBMS ภายในองค์กรไปยัง Open Source RDBMS บน CLOUD
ในส่วนที่ 2 ของบล็อกนี้ ฉันจะกล่าวถึงการคืนค่าและกู้คืนข้อมูลสำรองของ Postgre
ใช้แท็บคำติชมเพื่อแสดงความคิดเห็นหรือถามคำถาม คุณยังแชทตอนนี้เพื่อเริ่มการสนทนาได้
เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับบริการฐานข้อมูลของเรา


