สมมติว่าเราต้องการออกแบบอัลกอริธึมเพื่อทำให้เป็นอนุกรมและดีซีเรียลไลซ์ทรีการค้นหาแบบไบนารี การทำให้เป็นอนุกรมคือกระบวนการของการแปลงบางสิ่ง (โครงสร้างข้อมูลหรืออ็อบเจ็กต์) เป็นลำดับของบิต เพื่อให้สามารถเก็บไว้ในไฟล์หรือบัฟเฟอร์หน่วยความจำ หรือส่งผ่านลิงก์การเชื่อมต่อเครือข่าย ซึ่งสามารถสร้างขึ้นใหม่ได้ในภายหลังว่ากระบวนการนั้นคือการดีซีเรียลไลเซชัน
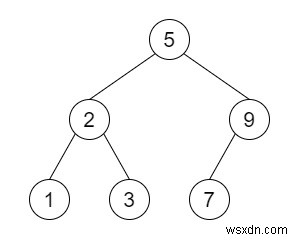
ดังนั้น หากอินพุตเป็น [5,2,9,1,3,7] เอาต์พุตจะเป็นเอาต์พุตแบบอนุกรม 5.2.9.1.3.7.N.N.N.N.N.N.N.N.N.N.N.N.N.N.N.N.N.N.N.N.N.N.N. (การข้ามเส้นทาง)
เพื่อแก้ปัญหานี้ เราจะทำตามขั้นตอนเหล่านี้ -
-
กำหนดฟังก์ชัน serialize() สิ่งนี้จะหยั่งราก
-
res :=รายการใหม่
-
กำหนดหนึ่งคิวและแทรกรูท
-
ขณะที่คิวไม่ว่างให้ทำ
-
ขณะที่คิวไม่ว่างให้ทำ
-
ปัจจุบัน :=คิว[0]
-
แทรกกระแสที่ส่วนท้ายของความละเอียด
-
ลบองค์ประกอบแรกออกจากคิว
-
ถ้ากระแสไม่เป็นศูนย์แล้ว
-
ออกจากวง
-
-
-
หากกระแสเป็นโมฆะ
-
ออกจากวง
-
-
ถ้า current.left ไม่เป็นโมฆะ
-
แทรก current.left ที่ท้ายคิว
-
-
มิฉะนั้น
-
แทรกไม่มีที่ท้ายคิว
-
-
ถ้า current.right ไม่เป็นโมฆะ
-
แทรก current.right ที่ท้ายคิว
-
-
มิฉะนั้น
-
แทรกไม่มีที่ท้ายคิว
-
-
-
s:=สตริงว่าง
-
สำหรับฉันในช่วง 0 ถึงขนาดของความละเอียด ทำ
-
ถ้า res[i] ไม่ใช่ศูนย์ แล้ว
-
s :=s concatenate res[i].data
-
-
มิฉะนั้น
-
s :=s ต่อ "N"
-
-
ถ้าฉันมีขนาดเท่ากับ res -1 แล้ว
-
ออกจากวง
-
-
s :=s concatenate "."
-
-
ผลตอบแทน s
-
กำหนดฟังก์ชัน deserialize() นี่จะใช้ข้อมูล
-
data :=รายการส่วนหลังการหารข้อมูลโดยใช้จุด
-
stack :=รายการใหม่
-
ถ้า data[0] เหมือนกับ 'N' แล้ว
-
กลับไม่มี
-
-
root :=สร้างโหนดใหม่ด้วย data data[0]
-
แทรกรูทที่ส่วนท้ายของสแต็ก
-
ผม :=1
-
ปัจจุบัน :=0
-
ในขณะที่ฉัน <ขนาดของข้อมูล ทำ
-
ซ้าย:=เท็จ
-
ถ้า data[i] ไม่เหมือนกับ 'N' แล้ว
-
temp :=สร้างโหนดใหม่ด้วย data data[i]
-
stack[current].left :=ชั่วคราว
-
ใส่ temp ที่ส่วนท้ายของ stack
-
-
มิฉะนั้น
-
stack[current].left :=ไม่มี
-
-
ผม :=ผม + 1
-
ถ้า data[i] ไม่เหมือนกับ 'N' แล้ว
-
temp :=สร้างโหนดใหม่ด้วย data data[i]
-
stack[current].right :=ชั่วคราว
-
ใส่ temp ที่ส่วนท้ายของ stack
-
-
มิฉะนั้น
-
stack[current].right :=ไม่มี
-
-
ปัจจุบัน :=ปัจจุบัน + 1
-
ผม :=ผม + 1
-
-
คืนค่ารูท
ตัวอย่าง
ให้เราดูการใช้งานต่อไปนี้เพื่อความเข้าใจที่ดีขึ้น -
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, data, left = None, right = None):
self.data = data
self.left = left
self.right = right
def insert(temp,data):
que = []
que.append(temp)
while (len(que)):
temp = que[0]
que.pop(0)
if (not temp.left):
if data is not None:
temp.left = TreeNode(data)
else:
temp.left = TreeNode(0)
break
else:
que.append(temp.left)
if (not temp.right):
if data is not None:
temp.right = TreeNode(data)
else:
temp.right = TreeNode(0)
break
else:
que.append(temp.right)
def make_tree(elements):
Tree = TreeNode(elements[0])
for element in elements[1:]:
insert(Tree, element)
return Tree
def print_tree(root):
#print using inorder traversal
if root is not None:
print_tree(root.left)
print(root.data, end = ', ')
print_tree(root.right)
class Codec:
def serialize(self, root):
res =[]
queue = [root]
while queue:
while True and queue:
current = queue[0]
res.append(current)
queue.pop(0)
if current:
break
if not current:
break
if current.left:
queue.append(current.left)
else:
queue.append(None)
if current.right:
queue.append(current.right)
else:
queue.append(None)
s=""
for i in range(len(res)):
if res[i]:
s+=str(res[i].data)
else:
s+="N"
if i == len(res)-1:
break
s+="."
return s
def deserialize(self, data):
data = data.split(".")
stack = []
if data[0]=='N':
return None
root = TreeNode(int(data[0]))
stack.append(root)
i = 1
current = 0
while i <len(data):
left= False
if data[i] !='N':
temp = TreeNode(int(data[i]))
stack[current].left = temp
stack.append(temp)
else:
stack[current].left = None
i+=1
if data[i] !='N':
temp = TreeNode(int(data[i]))
stack[current].right = temp
stack.append(temp)
else:
stack[current].right = None
current+=1
i+=1
return root
ob = Codec()
root = make_tree([5,2,9,1,3,7])
ser = ob.serialize(root)
print('Serialization:',ser)
print_tree(ob.deserialize(ser)) อินพุต
[5,2,9,1,3,7]
ผลลัพธ์
Serialization: 5.2.9.1.3.7.N.N.N.N.N.N.N 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 9,


