Python มีไลบรารี่จำนวนมากสำหรับการวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลและการแสดงภาพ โดยส่วนใหญ่เป็น numpy, pandas, matplotlib, seaborn เป็นต้น ในส่วนนี้ เราจะพูดถึงไลบรารี pandas สำหรับการวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลและการแสดงภาพ ซึ่งเป็นไลบรารีโอเพนซอร์สที่สร้างขึ้นบน numpy
ช่วยให้เราสามารถวิเคราะห์และทำความสะอาดข้อมูลและเตรียมข้อมูลได้อย่างรวดเร็ว นอกจากนี้ Pandas ยังมีฟีเจอร์การแสดงภาพในตัวจำนวนมาก ซึ่งเราจะดูด้านล่าง
การติดตั้ง
ในการติดตั้งแพนด้า ให้รันคำสั่งด้านล่างในเทอร์มินัลของคุณ -
pipinstall pandas
หรือมีอนาคอนด้าใช้
condainstall pandas
แพนด้า-DataFrames
กรอบข้อมูลเป็นเครื่องมือหลักเมื่อเราทำงานกับแพนด้า
รหัส −
import numpy as np import pandas as pd from numpy.random import randn np.random.seed(50) df = pd.DataFrame(randn(6,4), ['a','b','c','d','e','f'],['w','x','y','z']) df
ผลลัพธ์
| | w | x | y | z |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | -1.560352 | -0.030978 | -0.620928 | -1.464580 |
| b | 1.411946 | -0.476732 | -0.780469 | 1.070268 |
| c | -1.282293 | -1.327479 | 0.126338 | 0.862194 |
| d | 0.696737 | -0.334565 | -0.997526 | 1.598908 |
| e | 3.314075 | 0.987770 | 0.123866 | 0.742785 |
| f | -0.393956 | 0.148116 | -0.412234 | -0.160715 |
แพนด้า-ไม่มีข้อมูล
Weare จะได้เห็นวิธีที่สะดวกในการจัดการกับ data inpandas ที่หายไป ซึ่งจะถูกเติมด้วย 0 หรือ nan โดยอัตโนมัติ
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from numpy.random import randn
d = {'A': [1,2,np.nan], 'B': [9, np.nan, np.nan], 'C': [1,4,9]}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
df ผลลัพธ์
| | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0 | 9.0 | 1 |
| 1 | 2.0 | น่าน | 4 |
| 2 | น่าน | น่าน | 9 |
ดังนั้นเราจึงมีค่าหายไป 3 ค่าด้านบน
df.dropna()
| | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0 | 9.0 | 1 |
df.dropna(axis = 1)
| | C |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 4 |
| 2 | 9 |
df.dropna(thresh = 2)
| | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0 | 9.0 | 1 |
| 1 | 2.0 | น่าน | 4 |
df.fillna(value = df.mean())
| | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0 | 9.0 | 1 |
| 1 | 2.0 | 9.0 | 4 |
| 2 | 1.5 | 9.0 | 9 |
แพนด้า − นำเข้าข้อมูล
เรากำลังจะไปอ่านไฟล์ csv ซึ่งจัดเก็บไว้ในเครื่องของเรา (ในกรณีของฉัน) หรือเราสามารถดึงข้อมูลจากเว็บได้โดยตรง
#import pandas library
import pandas as pd
#Read csv file and assigned it to dataframe variable
df = pd.read_csv("SYB61_T03_Population Growth Rates in Urban areas and Capital cities.csv",encoding = "ISO-8859-1")
#Read first five element from the dataframe
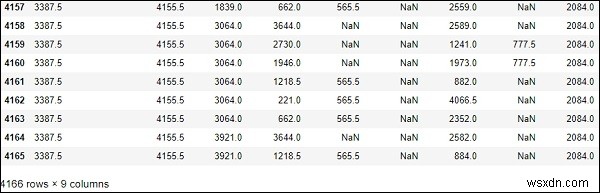
df.head() ผลลัพธ์
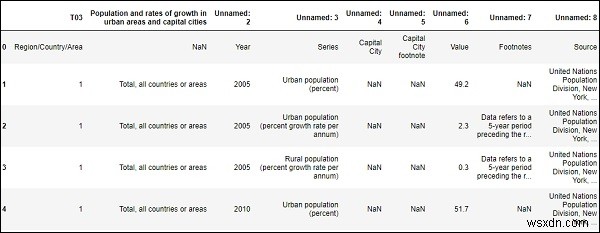
เมื่อต้องการอ่านจำนวนแถวและคอลัมน์ใน dataframe หรือไฟล์ csv ของเรา
#Countthe number of rows and columns in our dataframe. df.shape
ผลลัพธ์
(4166,9)
แพนด้า − Dataframe Math
Operationson dataframes สามารถทำได้โดยใช้เครื่องมือต่างๆ ของ pandas forstatistics
#To computes various summary statistics, excluding NaN values df.describe()
ผลลัพธ์
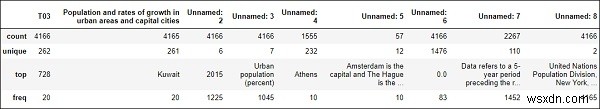
# computes numerical data ranks df.rank()
ผลลัพธ์
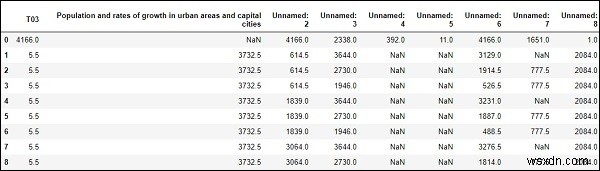
.....
.....
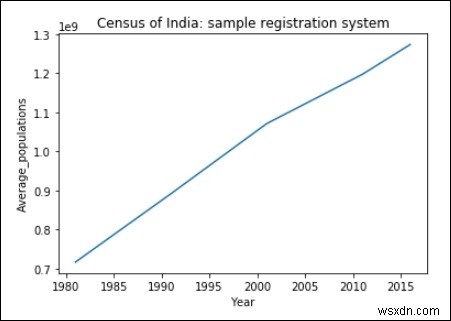
หมีแพนด้า − กราฟพล็อต
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
years = [1981, 1991, 2001, 2011, 2016]
Average_populations = [716493000, 891910000, 1071374000, 1197658000, 1273986000]
plt.plot(years, Average_populations)
plt.title("Census of India: sample registration system")
plt.xlabel("Year")
plt.ylabel("Average_populations")
plt.show() ผลลัพธ์
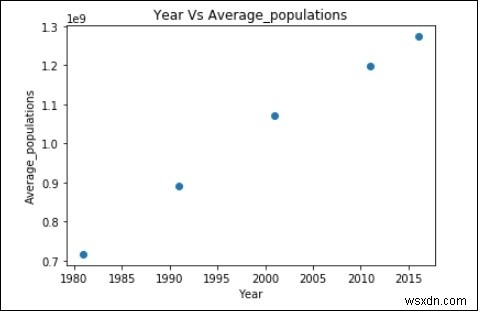
พล็อตกระจายของข้อมูลด้านบน:
plt.scatter(years,Average_populations)
ฮิสโตแกรม:
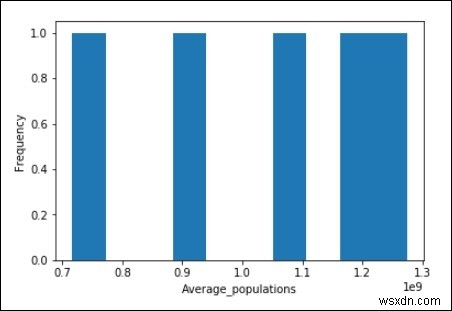
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Average_populations = [716493000, 891910000, 1071374000, 1197658000, 1273986000]
plt.hist(Average_populations, bins = 10)
plt.xlabel("Average_populations")
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
plt.show() ผลลัพธ์